How LoRa/ LoRaWAN devices increase IoT adoption
LoRa and LoRaWAN have disrupted the IoT industry with their exceptional low-power long-range communication capabilities. Before continuing with the topic, let us first understand the difference between LoRa and LoRaWAN.
What is the difference between LoRa and LoRaWAN?
LoRa is the wireless modulation technique based on the Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS) technology. At the same time, LoRaWAN is the Media Access Control (MAC) layer protocol built on top of LoRa modulation. We have seen AM radio stations where the AM signals were present even in the no man’s land and far away from the station. Even this used long-range communication but not only were the transmitters massive but also emitted kilowatt of energy. However, with LPWAN, obeying all the physics laws, we have achieved low-power and long-range of up to a few kilometers.

It is easy to understand the reason behind the wide adoption of LoRa(WAN) in deploying IoT applications requiring long-range communication. The long-range and low-power is achieved by playing with the bandwidth of the communication. As we know, when the bandwidth and channel capacity are decreased, there is an increase in the range of communication. Several other reasons for adopting LoRa(WAN) include deep indoor penetration, license-free spectrum, high capacity, end-to-end security, and low cost.
What kind of IoT applications run on LoRaWAN?
In general, the technology lends itself well to industrial internet of things applications due to its long-range and low cost with the advantage of geolocation. LoRaWAN is currently used for several IoT applications involving monitoring and control of connected devices from a longer distance. IoT applications built upon LoRaWAN include smart farms, smart waste bins, airport tracking, and even LoRa in space.
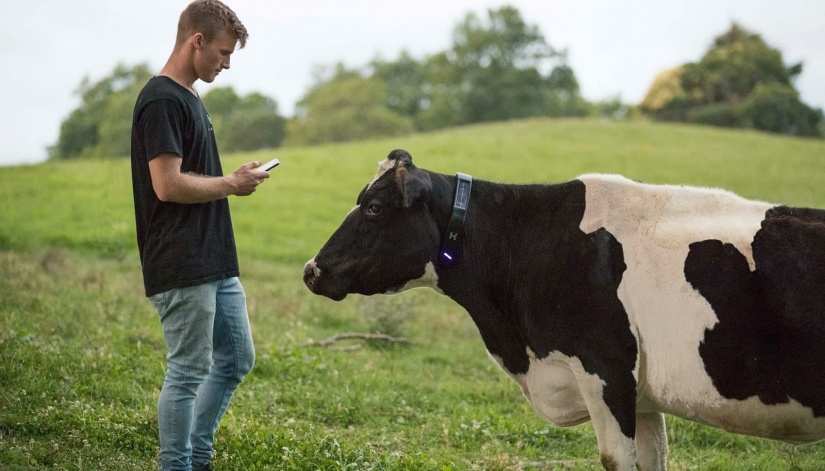

(Image Credit: Nanalyze)
To understand the application of LoRaWAN in IoT, let us take an example of cattle tracking using LoRaWAN. The power of LoRaWAN in the smart agriculture industry has increased in recent years. An interesting example is cattle tracking. This involves a solar-powered collar and a smartphone app that will help a farmer track cattle even from long-range distances. The system guides cows about the land, creates a virtual fence, senses heat, and automatically drafts the cow. This is achieved using LoRaWAN even when there is no mobile connectivity in the area.
LPWAN technology
This LPWAN technology (low-power wide-area network) provides reliable connectivity with long-range support, unlike other connectivity options like Cellular, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi. The ability to transmit information wirelessly over a long-range utilizing little power has been the primary reason for the wide adoption of LoRaWAN in IoT. Some of the LoRa-based sensors available in the market come with long battery life and an easy-to-use setup. Along with this comes the security aspect of the technology, which can become a concern for mass adoption. LoRaWAN is one of the most secure systems that operate on authentication and encryption, which are mandatory network steps. Still, it is crucial to keep the security keys safe.
View the full range of LoRaWAN products in the Electromaker shop.
The Future of IoT with LoRaWAN
The key features of low-cost, long-range, and low-range make it the most desirable wireless connectivity option in industrial and commercial IoT applications. It also solves several real-life problems related to monitoring and tracking in smart cities, smart agriculture, and logistics applications to improve users’ quality of life. The increasing market and growing ecosystem of LoRaWAN technology have forced the manufacturer to develop new IoT devices, gateways, end nodes, and sensors that continue to drive the adoption of LoRa and LoRaWAN.
LoRa and LoRaWAN devices market size is forecasted to reach $6.2 billion by 2026, and it is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 36.5% during 2021-2026. The predictions have an exponential increase in the deployment of LoRa-based sensors and end devices to the smart cities and agriculture industry. The disruptive technology can be compared with SigFox, another LPWAN but has several restrictions on end devices, payload length, and message limitations. The future of LoRaWAN in IoT appears to be very bright because it already exists in more than 100 countries, supported by over 70 network operators being the central non-cellular LPWAN ecosystem.

(Image Credit: Eckovation)
With so many upsides, there are also many challenges to the implementation of LoRaWAN. Some of this includes the geolocation of end devices, a GPS-based solution that can be pricey, and increased energy consumption. The technology requires low network hardware and has a relatively simple architecture that has reduced the cost of implementation significantly with low energy consumption.
Final Thoughts
Even though there are so many network options available for IoT implementation, it is very important to choose the right one that caters to the needs and requirements of the application. It is also essential to understand the ecosystem and support from the community to smoothly adopt the technology to the IoT industry. The initiative to introduce new devices and applications in smart agriculture has generated opportunities for adopting the LoRaWAN network in the next decade.
Summarizing the benefits of LoRaWAN include the deep indoor penetration that provides deep indoor coverage that can cover multi-floor buildings and the high capacity of LoRaWAN Network to handle millions of messages from the gateways. Also, with the exciting feature comes the end-to-end security that ensures secure communication between the end device and the application server using AES-128 encryption.
If you plan to adopt LoRaWAN to your application, it is essential to note that the technology is not suited for real-time data and does not want to detect rapid changes. There is also a limitation on the size of the payload that the user should not send JSON or plain (ASCII) text but encode the data as binary data. The open standard of LoRaWAN technology is supported by the Things Network, which will help the early adopter build an application using the console and guides. These are some of the reasons for the increased adoption of LoRa/LoRaWAN in the IoT industry.
View the full range of LoRaWAN products in the Electromaker shop.































Leave your feedback...