Mini Robot Mic Swarms: The Future of Audio Capture for Makers?
Isolating individual voices in a bustling room has always been a daunting challenge. Whether it's a lively board meeting, a bustling cafe, or a podcast recording, distinguishing one voice from the cacophony of conversations can be a Herculean task. Virtual meeting platforms offer the convenience of a mute button, allowing moderators to focus on a single speaker.
However, in physical spaces, the challenge intensifies. But what if technology could offer a solution, enabling us to 'mute' the background chatter and hone in on the voice we want to hear?
Enter Robotic 'Acoustic Swarms'
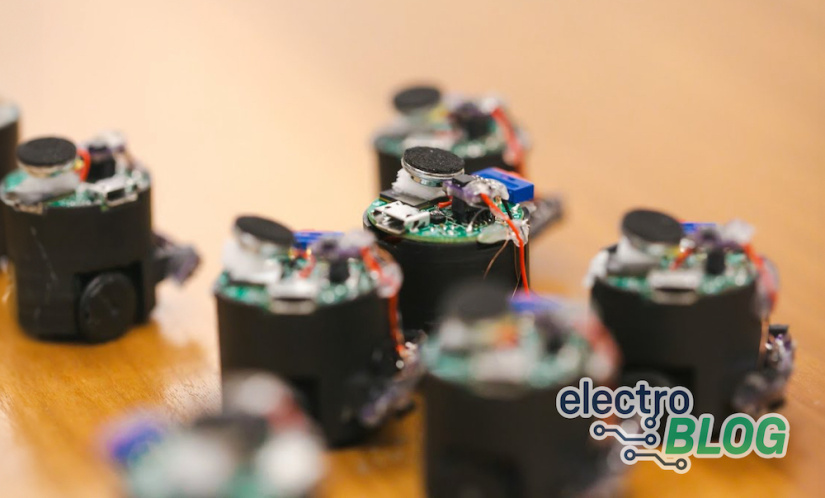
Imagine a system of microphones, not stationary or fixed, but moving dynamically, reminiscent of a swarm of pint-sized Roombas. These aren't your typical microphones. They spring into action, deploying strategically across a room, and adapting to its unique audio dynamics. During a board meeting, for instance, instead of the conventional central microphone setup, these roving mics could take center stage, offering unparalleled control over the room's audio landscape.
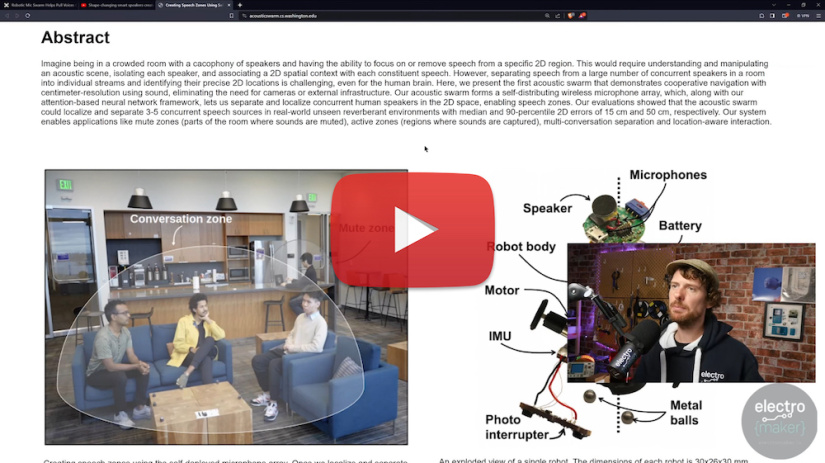
Watch Ian discuss Robotic 'Acoustic Swarms' in this episode of The Electromaker Show
How Does It Work?
This innovative "acoustic swarm" doesn't just differentiate voices; it pinpoints their exact locations within a room. And the most impressive part? It achieves this monumental task purely based on sound, eliminating the need for cameras or visual cues. Each microphone, about an inch in diameter, is designed to return to its charging station post-use, ensuring the system remains portable and adaptable to various settings.
Technical Insights
The prototype of this groundbreaking system comprises seven autonomous miniature robots, each functioning in harmony with the others. Using high-frequency sound, akin to the echolocation techniques employed by bats, these robots navigate their surroundings, especially tables, adeptly avoiding drop-offs. Their primary objective? To position themselves in a manner that ensures maximum audio accuracy.
Spacing plays a pivotal role in this system. By maintaining a significant distance between each robotic unit, the system can effectively create specific audio zones and mute undesired sounds. When a speaker vocalizes, the sound waves reach each microphone at varying intervals. The greater the distance between the microphones, the easier it becomes to triangulate the speaker's location and isolate their voice from the ambient noise. Traditional smart speakers, despite having multiple microphones, often fall short in this aspect due to the limited spacing between them.
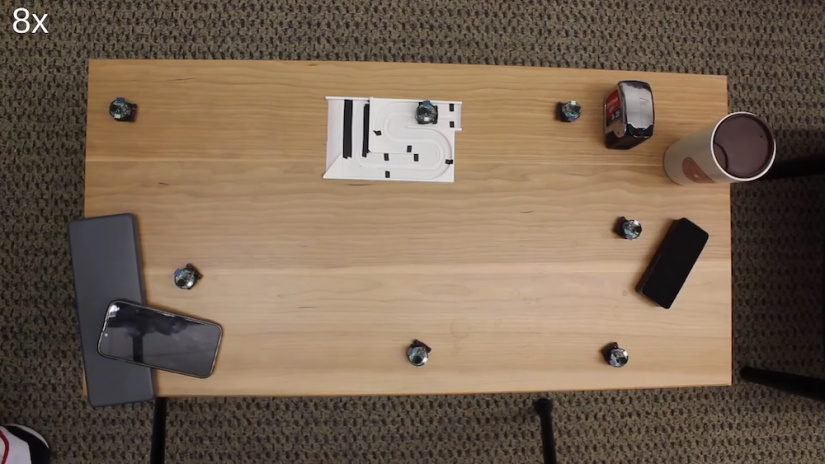
By maintaining a significant distance between each robotic unit, the system can effectively create specific audio zones and mute undesired sounds
As paper co-author Tuochao Chen says, "If I have one microphone a foot away from me, and another two feet away, my voice will reach the closer microphone first. If another individual is nearer to the farther microphone, their voice will arrive there first." Chen further explains the intricacies of the neural networks developed for this system, which utilize these time-delayed signals to segregate individual voices and map their positions within a space.
Neural Network and Voice Isolation
At the heart of this innovative system lies a sophisticated neural network, designed to process time-delayed signals and adeptly separate individual voices. By analyzing the slight differences in the time it takes for a voice to reach each microphone, the network can not only distinguish between multiple speakers but also accurately track their positions within a room.
"We developed neural networks that use these time-delayed signals to separate what each person is saying and track their positions in a space. So, in a room where four people are engaged in two separate conversations, our system can isolate any of the four voices and pinpoint their exact locations," said Chen.
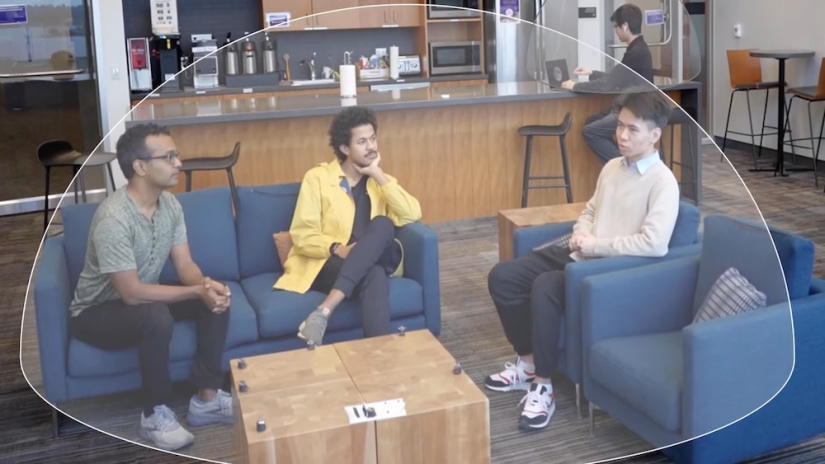

During tests in various environments, including kitchens, offices, and living rooms, the system showcased its prowess by differentiating voices situated within 1.6 feet of each other 90% of the time, without any prior knowledge of the number of speakers present. However, there's a slight delay in processing. Currently, it takes approximately 1.82 seconds to process 3 seconds of audio. While this delay is acceptable for livestreaming, it poses challenges for real-time calls.
Potential Applications
The implications of this groundbreaking technology stretch far and wide. Envision smart homes equipped with a well-spread microphone array, enabling vocal commands exclusively from individuals in designated "active zones." A voice-activated TV could be programmed to respond solely to commands from those seated on the couch, eliminating unintentional triggers from other conversations in the room.
Moreover, this technology could revolutionize virtual conferences. Imagine participating in a virtual meeting from a bustling cafe, without the need for individual microphones. While attendees would still require headphones to hear the conversation clearly, the robotic microphone swarm would ensure their voices are captured crisply and clearly, irrespective of the ambient noise.
While this might seem like a niche application, the potential is vast. The research team envisions more advanced microphone robots capable of navigating entire rooms, not just tables. They're also exploring the possibility of using these robots to emit sounds, creating real-world "mute" and "active" zones. This would allow individuals in different parts of a room to hear their personalized audio feed, enhancing the overall auditory experience.
Though still in its nascent stages, the concept is undeniably captivating. The prospect of enlivening corporate meetings with tiny robots skittering around, all in the pursuit of impeccable audio, is both intriguing and promising.
If more information on Creating Speech Zones with Self-distributing Acoustic Swarms visit the Acoustic Swarms microsite.
Did you enjoy this article?
Make sure you subscribe to The Electromaker Show for similar content and subscribe to our monthly newsletter!

























Leave your feedback...