Complete Guide to Proximity Sensors
In the maker world, there are tons of different components to help you complete your projects. You can find anything from simple LEDs to digital-to-analogue converters (DACs), maker boards, microcontrollers, and everything in between. Proximity sensors are excellent for a variety of purposes. Learn all about proximity sensors, from what they are to how they work, and check out the best proximity sensors on the market!
What Are Proximity Sensors?
 Credit: Wikipedia Commons
Credit: Wikipedia Commons
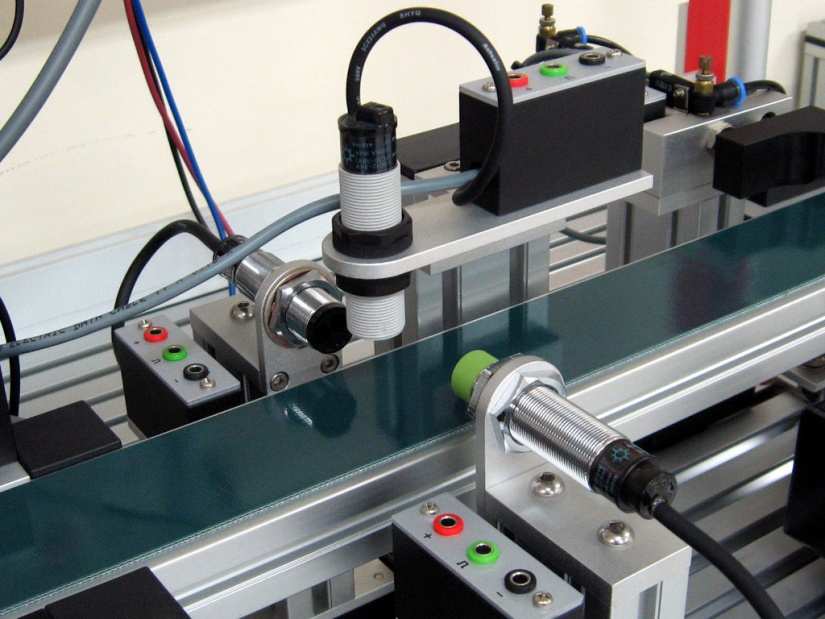
As the name suggests, a proximity sensor is a device capable of detecting objects close by without making physical contact. Instead, proximity sensors utilize a non-contact form of monitoring a physical presence. Typically, you’ll find electromagnetic or infrared technology onboard for sensing a change in field or state. However, sensor types do vary.
What is a proximity sensor: A proximity sensor is a device capable of detecting nearby physical objects through non-contact methods.
How Do Proximity Sensors Work?
A proximity sensor features two main components: a transmitter (the proximity sensor) and a target (the object being sensed). The transmitter emits some sort of signal (magnetic, electrical, infrared, sound, etc.). Then there’s some sort of change in the state, the sensor detects that presence.
What Are Common Real-world Applications of Proximity Sensors - How Are Proximity Sensors Used?
Image credit: via Wikipedia Commons
So how are proximity sensors actually used? Commonly, you’ll find proximity sensing technology used for manufacturing such as bottling and canning, as well as recycling. For instance, proximity sensors may be used for counting bottles at a bottling facility or positioning in a manufacturing plant to ensure that items on a conveyor belt are properly situated.
However, there are some more relatable examples that might pertain to your life. Many newer automobiles sport lane detection technology. Chances are, if you’ve got a newer vehicle you’re benefiting from lane monitoring systems that are powered by proximity sensors.
Additionally, mobile phones often feature proximity sensors baked in. Contactless sensing is regularly used in cell phones. In mobile devices, proximity sensors can turn off your phone’s screen while on a call to prevent, say, hitting the end call or mute button. Alternatively, proximity sensors can provide face-unlock capabilities.
Real-world applications of proximity sensors:
- Manufacturing (i.e. bottling, canning, etc.)
- Recycling
- Self-driving cars (i.e. lane detection/monitoring systems)
- Mobile devices (i.e. turning your phone screen off while your phone is pressed against your head on a call, face unlocking, etc.)
What Types of Proximity Sensors Exist?
 Image credit: via Wikipedia Commons
Image credit: via Wikipedia Commons
There are several different types of proximity sensors available. The most common varieties are magnetic proximity sensors, capacitive proximity sensors, photoelectric proximity sensors, and ultrasonic proximity sensors.
Magnetic proximity sensors: A magnetic proximity sensor relies on a magnetic field for sensing other objects. Because of their magnetism, this flavor of proximity sensor boasts a long detection range. Additionally, magnetic proximity sensors are capable of withstanding rough environments and therefore hold up well with heat, vibrations, or dust.
Infrared (IR) and passive infrared (PIR) proximity sensors: An IR proximity sensor emits infrared light from an IR LED emitter. When an object is nearby, it is reflected back at some angle, and the sensor calculates the distance based on the angle of reflection. IR contactless sensors are common in home security and may be used in day time or at night with low light. A passive infrared (PIR) sensor on the other hand doesn’t actually emit any infrared light. Instead, PIR sensors simply detect IR rays from other objects.
Capacitive proximity sensors: Capacitive proximity sensors rely on electrical capacitance for non-contact detection. Essentially, a capacitive type of proximity sensing device behaves similar to a capacitor. Usually, a metal plate in the sensor electrically interfaces with an oscillator circuit (which creates a regular electronic signal, generally a square or sine wave). The sensed object serves as the second capacitor plate, and an electrostatic (or stationary electric charge) field.
Photoelectric proximity sensors: Some of the most common proximity sensors utilize photoelectric sensing. Essentially, a photoelectric proximity sensor transmits light which is then reflected back at it from another object. When the beam of light is broken, a presence is sensed.
Ultrasonic proximity sensors: An ultrasonic proximity sensor detects sound. These are extremely common, especially in robotics projects such as self-driving cars. Often, Arduino-powered autonomous vehicles feature ultrasonic sensors. A high-frequency sound above the audible limit of human ears is transmitted (often around 25-50kHz). Then, that sound wave bounces off of nearby objects, and the receiver measures the distance between objects by calculating how long it takes for the sound to travel back. Many times, ultrasonic sensors feature the transmitter and receiver built into the same device with a design that resembles the adorable robot in “Wall-E.”
Inductive proximity sensors: An inductive proximity sensor uses non-contact measures for detecting metal objects. So how does an inductive proximity sensor work? Inductive contactless positioning and sensing devices are composed of a detector coil, also known as an induction loop. Usually, this is made up of insulated magnet wire wrapped around a highly-magnetic object like a ferrite ceramic rod. It’s linked with an electrical charge and, like a transistor, features a voltage. Power is applied for an alternating electrical current and a fluctuating magnetic field that creates eddy currents (or localized loops of electrical current within conductors). Conductivity is directly proportional to how close the target is to the sensor.
Common types of proximity sensors:
- Ultrasonic proximity sensors
- Photoelectric proximity sensors
- Capacitive proximity sensors
- Magnetic proximity sensors
- IR and PIR proximity sensors
- Inductive proximity sensors
Best Proximity Sensors You Can Buy
Although proximity sensors are commonly deployed in industrial applications, they’re equally great for maker projects. If your next do-it-yourself (DIY) project requires contactless sensing, you’ve got plenty of choices. Check out the best proximity sensors you can buy for all your DIYing needs!
Best Capacitive Proximity Sensor - DFRobot Capacitive Proximity Sensor
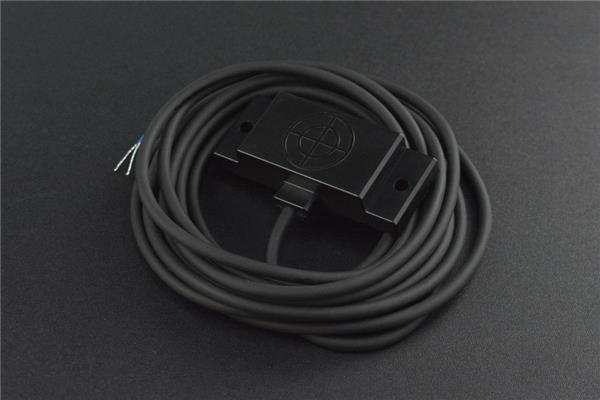

DFRobot makes an excellent capacitive proximity sensor. Whereas an inductive proximity sensor is limited to sensing metallic objects, this capacitive sensor can remotely monitor non-metallic objects. Since it’s a capacitive proximity sensor, this nifty component relies on an electrostatic field.
With an IP67 waterproof and dustproof rating, this DFRobot proximity sensor is well-suited to harsh environments. It delivers extremely accurate detection capabilities and, coupled with its ruggedization, works well for manufacturing or other demanding tasks. It includes a power supply range of 10-30 Volts (V), and a user-adjustable 1-10mm detection range.
Features:
- Capacitive contactless detection
- IP67 water- and dust-proofing
- Adjustable 1-10mm detection range
- 10-30V power supply
- Comprised of high-quality plastic
- Real-time object detection status indicator
Best Infrared Proximity Sensor - DFRobot Digital IR Proximity Sensor
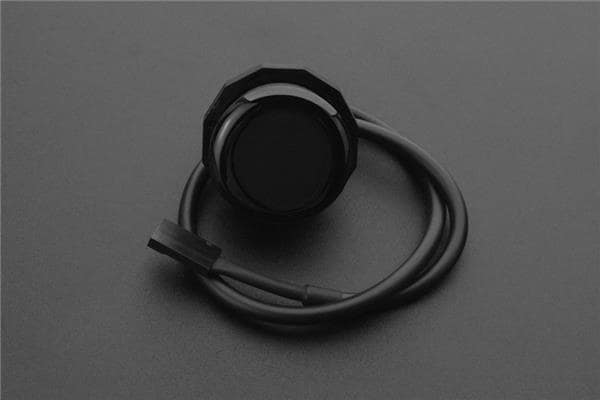

DFRobot also makes a solid digital infrared proximity sensor. It relies on IR sensing. There’s a generous 0-200cm detection distance alongside a real-time object detection status indicator. With an onboard 3-pin digital signal output data cable, this IR proximity sensor can interface with Arduino input/output expansion boards. As such, this is a spectacular option for makers.
In particular, it’s a good option for building DIY home security systems, smart home projects, robotics, and more. IP67 water- and dust-proofing plus an operating temperature of -10-60°C allows for use in rough conditions.
Features:
- IP67 water- and dust-proofing
- -10-60°C operating temperatures
- IR sensing technology
- Real-time object detection indicator
- 3-pin digital signal output data cable for Arduino interfacing
- 0-200cm adjustable detection distance
Best Passive Infrared (PIR) Sensor - Parallax Wide-angle PIR Sensor
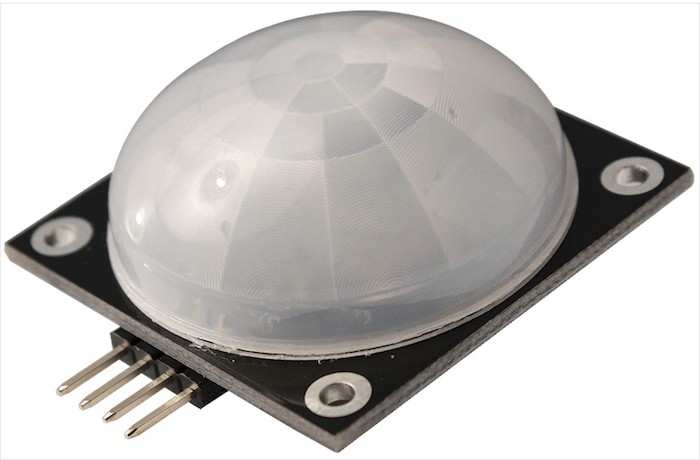

A passive infrared or PIR sensor is a fantastic choice for a variety of different remote sensing projects. This Parallax PIR sensor includes a super wide 180-degree angle of detection. It monitors motion by tracking changes in infrared levels transmitted by nearby objects. A built-in LED lights up when motion is detected for a visible readout of motion detection.
Features:
- 180-degree detection for a large field
- LED motion detection indicator
- Up to 30-foot range
- Night mode for low-light operation
- Great for smart home security systems, motion-activated lights, and more
- Passive infrared proximity detection
Best Ultrasonic Proximity Sensor - Parallax PING Ultrasonic Sensor
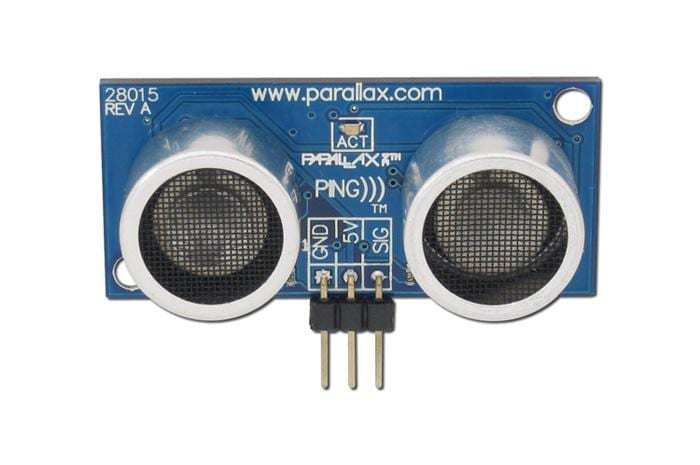

The Parallax PING ultrasonic sensor is an outstanding device to remotely monitor the distance between objects. It sports a transmitter and receiver baked onto one board. Parallax’s PING easily interfaces with common microcontroller units (MCUs) like Arduino boards.
There’s a solitary input/output (I/O) pin that emits an ultrasonic burst, then detects the returning echo and calculates the time for the signal to bounce back. It’s capable of contactless measurement ranging from 3cm to 3m. Pulse transmission and detection operates via one I/O pin. An onboard burst indicator LED provides visible measurement indications. Its 3-pin connector lets you hook the PING up to different maker boards and microcontrollers.
Features:
- Ultrasonic sensing technology
- 3cm-3m detection ranges
- LED burst indicator
- 3-pin connector for interfacing with maker boards and microcontrollers
- Single I/O pin ultrasonic burst transmission/detection
- Great for smart home automation/control projects, self-driving cars, etc.
Best Inductive Proximity Sensor - DFRobot Ring Inductive Proximity Sensor
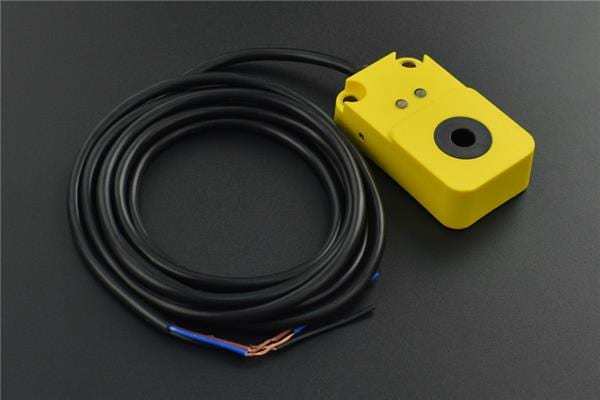

DFRobot offers several spectacular inductive proximity sensors in 8mm, 6mm, and 3mm hole diameters. These inductive contactless detection units feature 6-36V power supplies. With under 1ms response times (probably better than your gaming monitor), these proximity monitors are extremely accurate.
You’ll find built-in LED indicators for visible object detection status readouts. IP66 weatherproofing and operating temperatures between -25℃-65℃ make DFRobot’s inductive proximity sensors awesome options for industrial environments.
Features:
- 8mm, 6mm, 3mm hole diameter options
- 6-36V power supply
- Under 1ms response time for accurate object detection
- Great for sensing metal parts like nuts, screws, or washers
Best Long-range Infrared Proximity Sensor - SparkFun IR Proximity Sensor
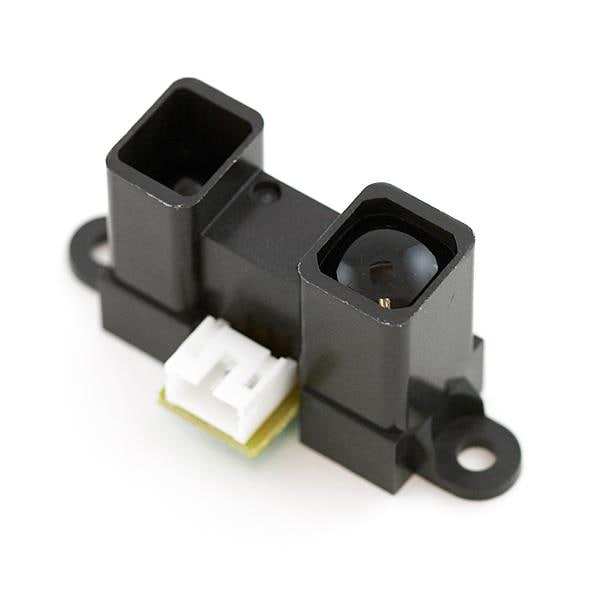

SparkFun provides an incredible IR proximity sensor. It boasts a long-range for exceptional object detection. There’s a supply voltage ranging from 4.5 to 5.5 Volts. This SparkFun IR proximity sensor can detect objects up to 5 feet away. There are loads of different applications for an infrared sensor including a DIY television remote.
Features:
- IR object detection
- 4.5-5.5V power supply
- Long-range - detects objects up to 5 feet away
While these are our favorite proximity sensors to satisfy your maker needs, there are plenty of other options available.
Complete Guide to Proximity Sensors - Final Thoughts
Proximity sensors are incredibly common and extremely useful. With industrial, automotive, manufacturing, and even consumer electronic applications, non-contact object detection has a ton of practicality.
Just as varied as the use cases of proximity sensors are the contactless sensing technologies themselves. You’ll find everything from magnetic, photoelectric, ultrasonic, capacitive, infrared, and passive IR sensors. There’s a slew of proximity sensors on the market for at-home DIYing from the likes of DFRobot, SparkFun, Parallax, and other manufacturers. Whether you want to build an autonomous vehicle, Arduino-powered robot, smart home security system, motion-detected light trigger, or something else entirely, a proximity sensor can help you achieve it.
Your turn: What everyday uses of proximity sensors have you noticed? How have you integrated proximity sensors into your DIY projects?




































Leave your feedback...