Build A Gps Tracker With Seeed Studio Xiao Esp32-s3
About the project
DIY Wi-Fi GPS tracker using Xiao ESP32-S3 + Neo-6M with geofencing and SMS alerts — no SIM card or GSM module needed.
Project info
Items used in this project
Story
In this project, you’ll build a compact Wi-Fi GPS tracker using the Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32-S3 microcontroller and a Neo-6M GPS module.
Unlike traditional GSM-based solutions, this tracker sends GPS location data over Wi-Fi to the GeoLinker cloud platform, where you can view routes, set geofencing zones, and get automated SMS alerts when boundaries are crossed — all without a SIM card or cellular service.
This project is ideal for makers, hobbyists, and IoT enthusiasts looking to monitor vehicles, pets, or assets with a low-cost, real-world tracking solution that leverages cloud APIs and offline buffering.
GPS tracker using the Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32-S3

GPS tracker using the Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32-S3
Key Features- No Cellular Service Required: Uses Wi-Fi to upload GPS coordinates to the cloud.
- Geofencing Alerts: Detects when your tracker leaves a predefined area.
- SMS Notifications: Sends location alerts via SMS when the geofence is breached.
- Offline Storage: Buffers location data when Wi-Fi is unavailable and syncs later.
- Real-Time Mapping: View routes and history on the GeoLinker dashboard.
- Free Tier Support: Includes a free allocation of location history and API usage.
CircuitDigest Cloud
CircuitDigest Cloud
How It WorksGPS Lock: The Neo-6M module receives satellite signals and computes latitude/longitude.
Data Parsing: XIAO ESP32-S3 reads GPS NMEA data over UART.
Cloud Upload: Coordinates are sent over Wi-Fi to GeoLinker at defined intervals.
Geofence Check: The system continuously calculates distance from the home location using the Haversine formula.
Alerts: If the tracker crosses the set radius, an SMS is triggered via the cloud API.
Offline Sync: If offline, GPS points are buffered and uploaded once connectivity returns.
Circuit Diagram
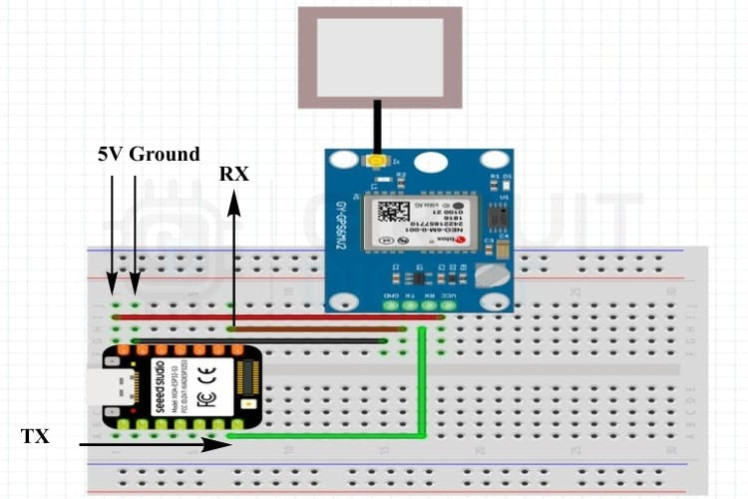
Circuit Diagram
Components NeededHardware
- Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32-S3
- Neo-6M GPS Module
- Breadboard & jumper wires
- External GPS antenna (for reliable reception)
- Software
- Arduino IDE
- Libraries: GeoLinker, TinyGPSPlus, WiFiClientSecure
Components
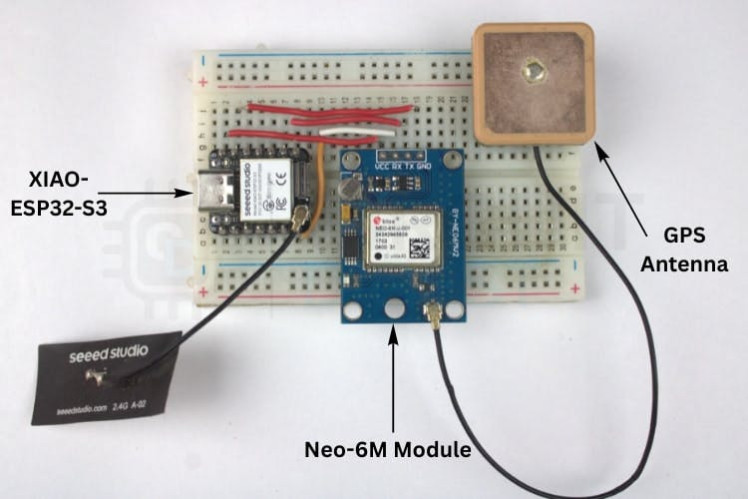
Components
Build Steps (Summary)- Wire the hardware: Connect the Neo-6M GPS module to the XIAO ESP32-S3 (TX/RX, power, GND).
- Sign up for GeoLinker: Create an account and generate an API key for uploading data and enabling SMS alerts.
- Configure your code: Load Wi-Fi credentials, API key, device ID, update interval, and geofence radius into the Arduino sketch.
- Upload & Test: Upload firmware and check location updates on the cloud dashboard.
- Vehicle tracking without cellular plans
- Pet or child safety geofencing
- Asset monitoring and route histories
- Offline-resilient location logging
Real Time Working
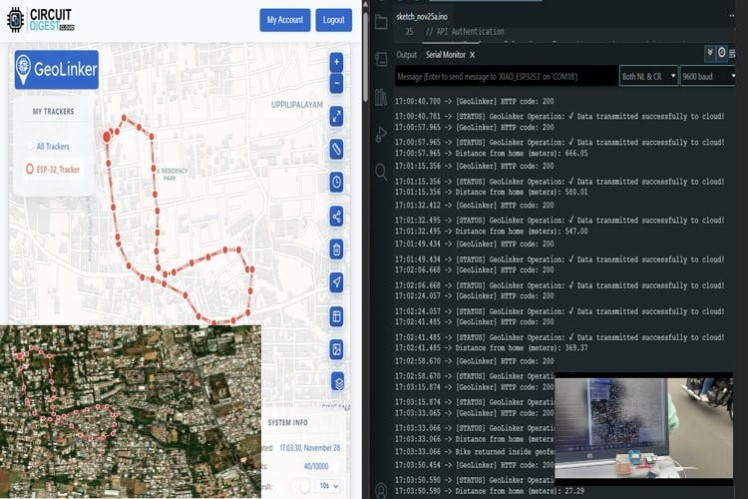
Real Time Working
What You’ll LearnThis project helps you explore:
- GPS integration with microcontrollers
- Wi-Fi communication and cloud APIs
- Geofencing logic and SMS triggers
- Offline data buffering for IoT reliability















Leave your feedback...