Arduino Dual-axis Solar Tracker: 40% More Power
About the project
Arduino-powered dual-axis solar tracking system using LDR sensors and servo motors boosts solar panel efficiency by up to 40% over a fixed.
Project info
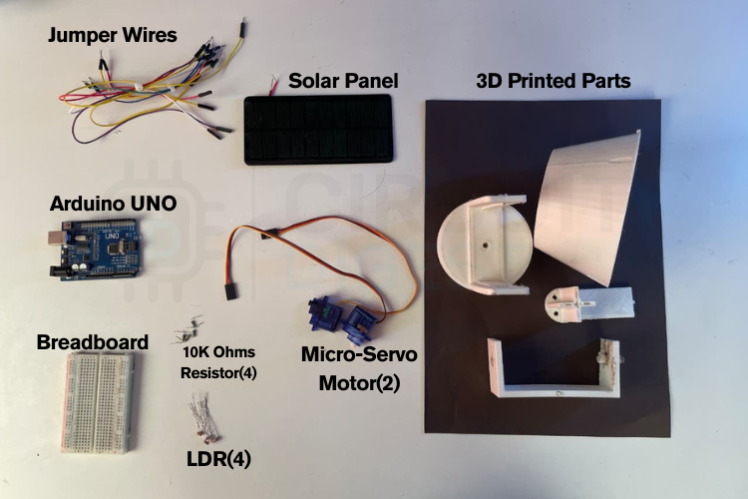
Items used in this project
Story
Build a dual axis solar tracker system using Arduino, LDR sensors & servo motors. Increase solar panel efficiency by 30-40%. Complete circuit diagram & code included.
Details
OverviewThis project demonstrates how to build an intelligent dual-axis solar tracking system that dramatically improves solar panel efficiency compared to fixed installations. By continuously adjusting the panel's orientation to face the sun throughout the day, this Arduino-based system can increase energy output by 30-40% over static panels.
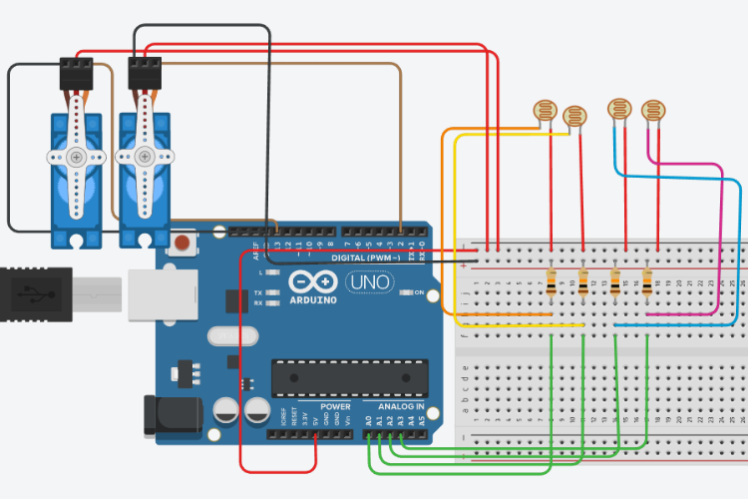
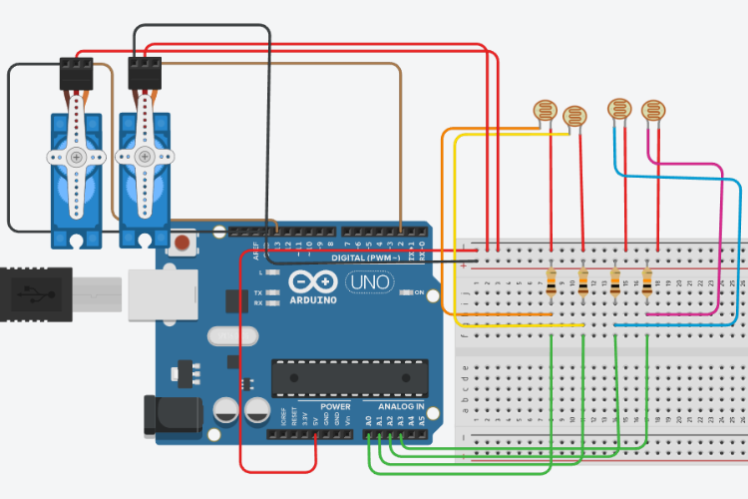
The tracker uses four light-dependent resistors (LDRs) arranged in a cross pattern to detect sunlight direction from all angles. An Arduino UNO processes these sensor readings and controls two servo motors—one for horizontal (azimuth) movement and one for vertical (elevation) adjustment. The system automatically enters standby mode during low-light conditions to conserve energy.
 Key Features
Key Features- Dual-axis tracking: Full horizontal and vertical solar tracking capability
- Real-time adjustment: Continuous sun position monitoring and panel repositioning
- Energy efficient: Automatic night mode to prevent unnecessary movement
- Low-cost components: Built with readily available Arduino parts
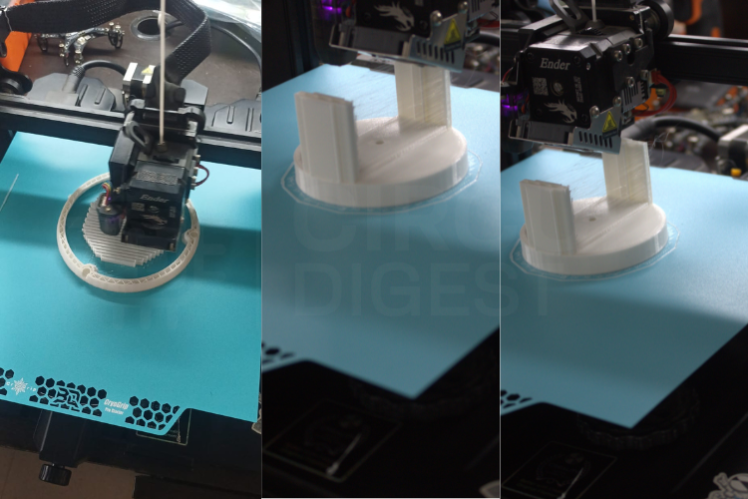
- Modular design: 3D-printed mechanical components for easy assembly
- Arduino UNO
- 4× LDR sensors (5mm)
- 2× Micro servo motors
- 4× 10kΩ resistors
- Solar panel
- Breadboard and jumper wires
 How It Works
How It WorksThe system employs a smart tracking algorithm that compares light intensity readings from the four LDR sensors positioned at the panel corners. When one side receives more sunlight than another, the Arduino calculates the difference and commands the appropriate servo motor to rotate the panel toward the brightest point.
The horizontal servo handles east-west positioning while the vertical servo adjusts north-south tilt. A tolerance threshold prevents unnecessary micro-adjustments, and sensor readings are averaged to reduce noise and improve stability.
 Build Details
Build DetailsAll mechanical components were 3D-printed for precise alignment and stable movement. The LDR sensors form voltage dividers with 10kΩ resistors, providing accurate analog readings to Arduino pins A0-A3. The servos connect to digital pins 2 and 13 for independent control.
The tracking algorithm continuously samples light levels, processes the data, makes positioning decisions, and actuates the servos—all within milliseconds. This rapid response ensures optimal panel alignment regardless of changing sun intensity throughout the day.
Applications
This dual-axis solar tracker is ideal for:
- Off-grid power systems require maximum efficiency
- Educational demonstrations of renewable energy optimisation
- Remote monitoring stations with a limited solar panel area
- DIY solar installations where space is constrained
The Dual Axis Solar Tracker System Using Arduino code, circuit diagrams, and 3D models are available in the project's GitHub repository for anyone interested in building their own sun-tracking solar system.

















Leave your feedback...