Effortless I²c Level Shifting: Pca9306 With Arduino Uno
About the project
Use the PCA9306 bidirectional level shifter to seamlessly connect 5V Arduino and 3.3V I²C devices — no software tweaks needed!
Project info
Items used in this project
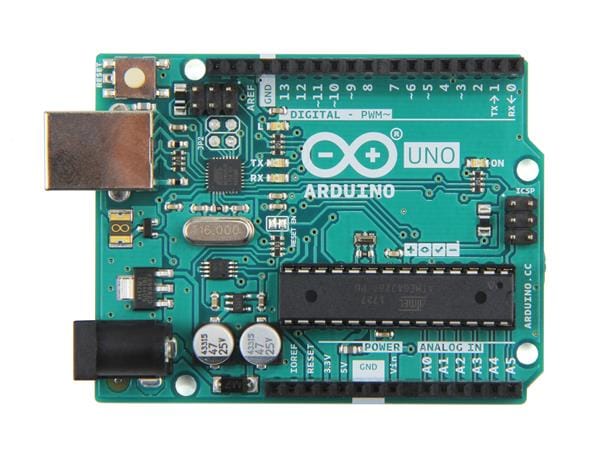
Hardware components
Story
When building embedded systems, mixing components that operate at different logic voltages can lead to unreliable communication or even hardware damage. One common challenge is interfacing 5V microcontrollers like the Arduino Uno with 3.3V sensors — especially when using the I²C protocol.
In this project, you’ll learn how to interface the PCA9306 bidirectional voltage-level translator with an Arduino Uno and a 3.3V I²C sensor. The PCA9306 makes it easy to bridge devices that speak different logic levels while preserving I²C protocol integrity.
PCA9306 Module with Arduino Uno

PCA9306 Module with Arduino Uno
What Is the PCA9306 Level Shifter?The PCA9306 is a compact bidirectional voltage-level translator designed specifically for I²C buses. It automatically adapts signals between a low-voltage side (e.g., 3.3V) and a high-voltage side (e.g., 5V), making it ideal for mixed-voltage systems.
Key characteristics include:
- Supports bidirectional I²C communication for both SDA and SCL lines.
- Automatic direction handling — no software configuration needed.
- Wide voltage range (VREF1: 1.0–3.6V, VREF2: 1.8–5.5V).
Unlike simple resistor dividers or unidirectional converters, the PCA9306 reliably preserves open-drain I²C signaling and adheres to timing and arbitration standards.
PCA9306 Pinout
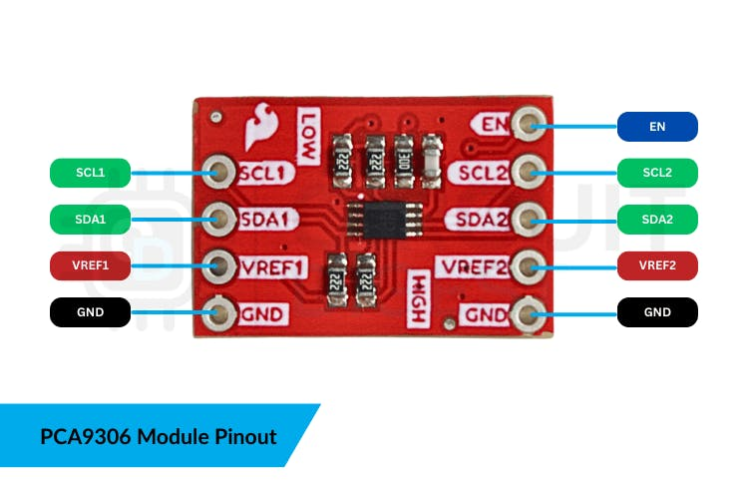
PCA9306 Pinout
How It Works: Pin OverviewHere’s a breakdown of the PCA9306 module and how its pins connect to different voltage domains:
- VREF1 — Reference voltage for the low-voltage side (typically 3.3V).
- VREF2 — Reference for the high-voltage side (typically 5V from Arduino).
- SCL1 / SDA1 — I²C lines on the low-voltage side (connected to the sensor).
- SCL2 / SDA2 — I²C lines on the high-voltage side (connected to Arduino).
- EN — Enable pin (must be tied HIGH to activate).
- GND — Common ground for both sides.
Wiring Diagram
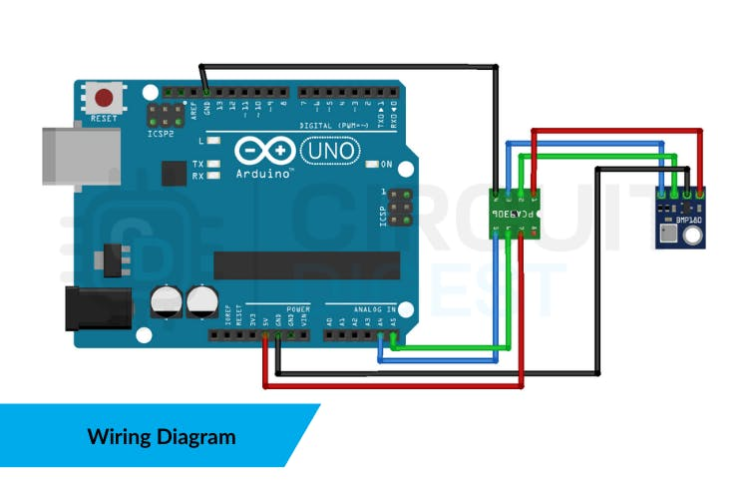
Wiring Diagram
Components RequiredTo complete this PCA9306 Module with Arduino Uno, you will need
- Arduino Uno — Your 5V logic microcontroller.
- PCA9306 Level Shifter Module — To translate between 5V and 3.3V logic
- 3.3V I²C Sensor (e.g., BMP180) — A device that communicates over I²C.
- Jumper Wires & Breadboard — For easy prototyping.
- USB Cable — For power and programming.
One of the biggest advantages of the PCA9306 is its simplicity. Once wired properly, no changes are required in your Arduino code to accommodate the level shifting. The level shifter transparently passes I²C data between devices.
Here’s a sample sketch using the BMP180 sensor library
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_BMP085.h>
Adafruit_BMP085 bmp;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("BMP180 Test");
if (!bmp.begin()) {
Serial.println("Sensor not found — check wiring!");
while (1);
}
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Temp: ");
Serial.print(bmp.readTemperature());
Serial.println(" °C");
Serial.print("Pressure: ");
Serial.print(bmp.readPressure());
Serial.println(" Pa");
Serial.println();
delay(2000);
}
This code initializes I²C communication and reads sensor data at intervals. The PCA9306 ensures safe voltage translation without requiring any code changes for level shifting.
Interfacing the PCA9306 Module with Arduino Uno
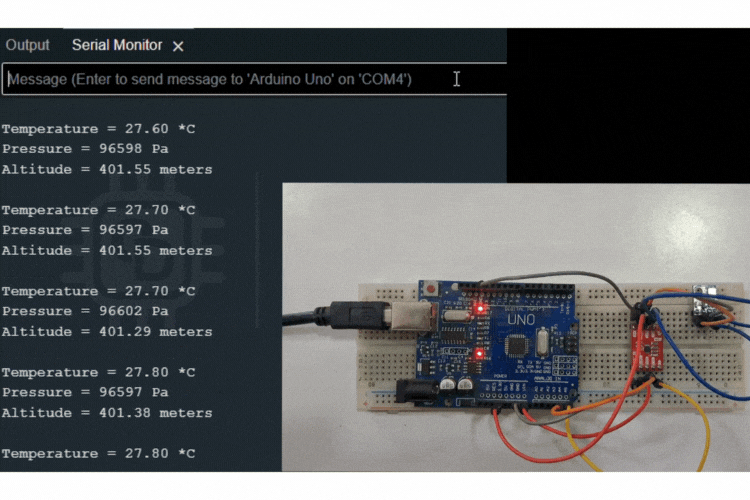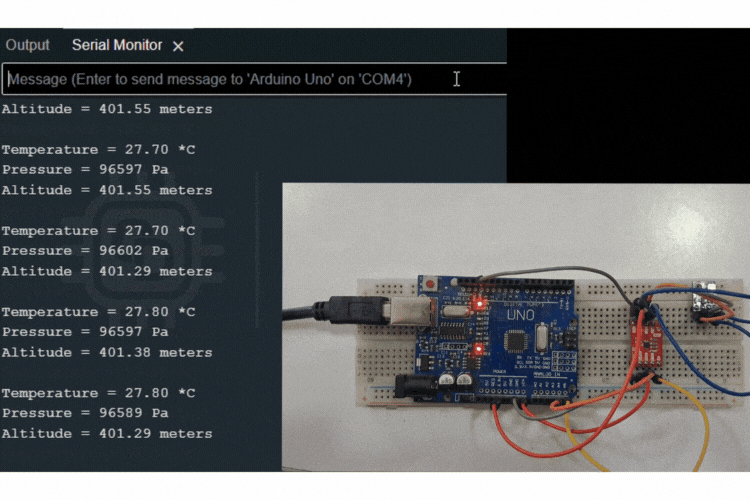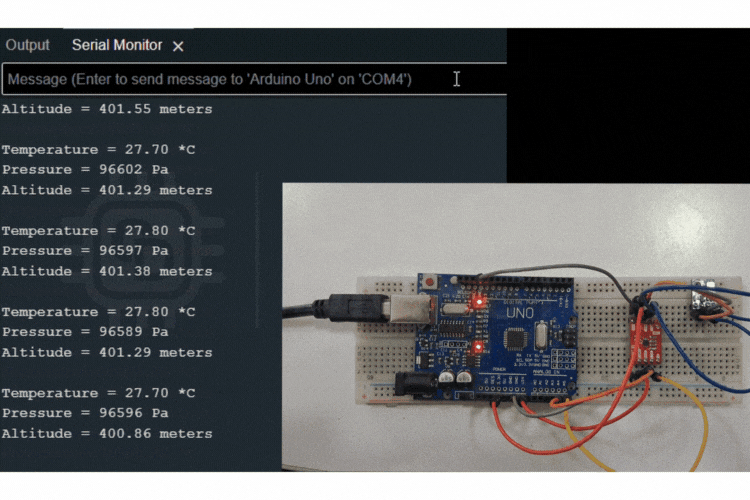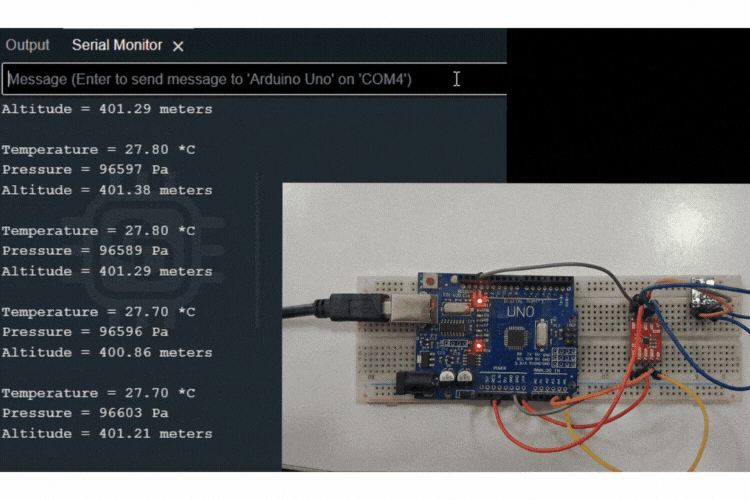
Interfacing the PCA9306 Module with Arduino Uno
Troubleshooting TipsHere are some tips if things don’t work as expected:
- Check pull-up resistors: Most PCA9306 modules include pull-ups only on the low-voltage side. The high side often relies on Arduino’s internal pull-ups.
- Ensure EN is tied high.
- Use short wires: Excessive bus capacitance can slow down I²C signals.
- Maintain common ground between all components.
This setup isn’t limited to one sensor — you can apply this technique to:
- Interfacing 3.3V environmental sensors with 5V boards.
- Connecting low-voltage EEPROMs to higher-voltage controllers
- Bridging I²C devices across different boards in embedded systems.
The PCA9306 level shifter unlocks reliable bidirectional I²C communication between devices operating at different logic levels. With simple wiring and no software overhead, it’s a powerful addition to any hobbyist or professional embedded project.
By combining solid hardware practices, clear wiring, and sensible troubleshooting, you can confidently expand the reach of your Arduino-based designs while maintaining signal integrity and device safety. For a variety of innovative IoT builds and tutorials using the Arduino, explore these Arduino project ideas
















Leave your feedback...